Basically, video compression is divided into two categories: lossless compression and lossy compression. Lossless video compression is achieved mainly via video trim/crop to remove unwanted video clips from video to reduce video size. Lossy video compression makes video file smaller mainly through video codec conversion and parameters adjustment. Therefore, if you need a lossless video codec, sorry to tell you that there is no 100% lossless video codec.
Don't be gloomy. There are visually lossless video codecs for you to shrink video file size with output quality almost equal to the original one. You can find out the best lossless video codecs (comparatively speaking) from the following video codecs comparison, which rounds up the currently most popular video codecs (incl. H264, MPEG-4, H265) for your reference.
Lossless Video Codec Decoder and Encoder
MacX Video Converter Free - 100% safe and free lossless video codec transcoder:
- Free transcode video codecs, from lossless to lossy codecs, VP9 to VP8, HEVC to H.264, etc.
- Convert between tons of video container formats, such as MKV to MP4, AVI to MOV, MOV to MP4.
- Compress videos with more efficent codec formats and save storage space.
- 180+ video and 14+ audio formats supported.
Table of Content
- Part 1. List of Top Lossless Video Codecs
- Part 2. Which Video Codec is Virtually Lossless in Video Compression?
- Part 3. FAQs about Lossless Video Codec Formats
#1. H.264
#2. MPEG-4
#3. H265 (HEVC)
#4. VP9
#5. AOMedia Video 1 (AV1)
Part 1. List of Top Lossless Video Codecs
Background knowledge does matter a lot in learning something new. The same applies to know the best lossless video codec. Prior to go directly to the best visually lossless video codecs, you'd better have a basic understanding about the current most popular video codecs and their advantages and disadvantages. Thus, it would be much easier for you to conclude the best virtually lossless video codecs. Certainly, you can skip this part and jump to the section you need if you know a thing or two about the top video codecs. If not, you're suggested to spend 2 mins here reading the brief introductions of best video codecs.
H.264
H264 is one of the most commonly used video compression standard for video recording, compression and distribution. Since H264 is jointly developed by ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (standard setter of H261, H262, H263) and ISO/IEC JTC1 Moving Picture Experts Group (standard setter of MPEG-1, MPEG-2, MPEG-4), H264 is also called MPEG-4 AVC or MPEG-4 Part 10. It's extended from H263, MPEG-4 Visual and extended to H265 (HEVC).
Unparalleled compatibility, accepted by almost any device, player and platform.
Keep good balance between file compression and quality, virtually lossless in quality.
The H264 file size of 4K/8K Ultra HD is comparatively large in size.

MPEG-4
MPEG-4 also a compression standard of audio and video digital data, absorbs a lot from its predecessors MPEG-1, MPEG-2 and others. Different from H264, MPEG-4 is an evolving standard, disintegrated into several parts, including MPEG-4 Part 2, MPEG-4 Part 10, MPEG-4 Part 14, MPEG-4 Part 16, etc.
Supported by most devices and platforms.
Produce excellent output quality, visually lossless.
The compression ability is still needed to get improved.
H265 (HEVC)
H265 (HEVC), the abbreviation of High Efficiency Video Coding (aks. MPEG-H Part 2), is a compression algorithm, much more efficient than its predecessor H264. When it comes to compare H265 with H264, the biggest difference lies in coding tree units. The pattern CTU sizes in HEVC can be extended from 16×16 pixel to 64×64 while H264 only has the power to support the block-size up to 16x16. Basically, HEVC offers around double compression ratio compared with H264, which makes it a primary choice to shrink and encode video to 4K/8K Ultra HD video.
High compression ratio, 2 times that of H264.
High effeciency without the expense of quality. Highest possible quality is guaranteed.
Higher demands on hardware configurations. The video codec compatibility leaves something to be desired.
VP9
VP9 is an open and royalty-free video codec from Google. It's the successor to VP8 and is designed to complete with HEVC lossless video codec format. VP9 codec is commonly used by Google platforms, such as YouTube. The lossless video codec format is mainly supported by web browsers, Android, and iOS. VP9 also allows lossless compression and is optimized for 1080p and 4K UHD. Netflix has used VP9 lossless video encoding for their catalog since 2016.
High compression ratio, 40 to 45% bitrate advantage over H.264.
VP9 lossless video codec is close to HEVC in efficiency.
Higher demands on hardware configurations. The lossless video codec requires more processing power to decode.
AV1
AOMedia Video 1 or AV1 in short is developed by replace MPEG format. It's an open source and license-free lossless video codec. AV1 codec can be encoded as MP4 and MKV. YouTube now supports AV1 codec for 8K video content streaming. Now more tech giants starts to support AV1, including Microsoft, Apple, Netflix, Amazon, Hulu, etc. Hardware providers such as Intel, AMD, ARM, and Nvidia also join AV1 lineup.
AV1 videos can be streamed in higher quality and faster.
AV1 lossless video codec is license-free.
Compatibility issues. Hardware support needs to be improved.
Video Codecs |
Definition |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
WMV |
the short form of Windows Media Video, WMV is a series of video codecs developed by Microsoft, with a purpose to replace QuickTime related tech standards and WAV/AVI file extension names. |
1. ASF container format to contain the encoded multimedia content. |
Obvious quality loss |
VP8 |
developed by Google, has something similar to H264, also a block-based transform coding format. It's usually contained by MKV or WebM container format with Vorbis and Opus audio. |
1. Royalty-free public license, no patent fees. |
1. Slightly lower quality than H264, visually no difference. |
XviD/DivX |
a video codec library with ability to abridge length file to smaller size while maintaining highest possible quality. As the successor to DivX, XviD is now in active with MPEG-4 ASP standard to encode video with .AVI file extension name. |
Excellent output quality |
1. Weak compression ability. |
MPEG-2 |
a video codec standard widely used in digital television broadcasting and DVD video. |
Excellent video quality |
1. Large in file size. |
MPEG-1 |
the predecessor of MPEG-2, used mainly in VCD. |
Excellent in quality |
Poor in size and compatibility |
After reading the above explainations of the most commonly used video codecs, you may have an overall understanding about the 8 video codecs. Yet, it's still hard to distinguish the delicate difference among some similar video codecs in respect of quality video compression ratio and file size. To make this clear, here we conduct a real test on these video codecs and use the actual test data to help you tell the specific differences among them.
Part 2. Which Video Codec is Virtually Lossless in Video Compression?
The test is conducted on an iMac (27-inch, 2011) with Mac OS X Yosemite operating system, alongside with 2.7GHz Intel Core i5 processor, AMD Radeon HD 6770M 512MB and 8GB 1333 MHz DDR3. And the video codec converter we use is the No.1 fast MacX Video Converter Pro (Intel/Nvidia/AMD HW accelerated). The input video is an MP4 video with AVC codec, 4m47s in length, 94.7 MB in size and 1280x720 in resolution. The test results are as follows:
Input Video: MP4 (AVC) 720p, 23FPS | File Size: 94.7MB; Duration: 4m47s |
||||||
Video Codecs |
File Size |
Compression Ratio |
Resolution |
Output Quality |
Compression Time |
Frame Rate |
74.6 MB |
21.22% |
1280x720 |
Virtually lossless |
8.3s |
23 FPS |
|
MPEG-4 |
164 MB |
Poor |
1280x720 |
Untouched quality |
45.54s |
23 FPS |
HEVC (H265) |
32.8 MB |
65.36% |
1280x720 |
Virtually lossless |
1m37.8s |
23 FPS |
WMV |
57.2 MB |
40% |
1280x720 |
Lossy quality |
18s |
30 FPS |
83.4 MB |
12% |
1280x720 |
Excellent quality |
3m13.67s |
23 FPS |
|
XviD/DivX |
177MB |
Poor |
1280x720 |
Untouched quality |
35.43s |
23 FPS |
MPEG-2 |
171 MB |
Poor |
1280x720 |
Intact quality |
26.47s |
23 FPS |
MPEG-1 |
168 MB |
Poor |
1280x720 |
Intact quality |
25s |
23 FPS |
From the above table, you can reach the conclusion that generally H264 is the best virtually lossless video codec with a good balance among quality, compression ratio and file size. More importantly, the video encoding speed is much faster than other codecs and also has better compatibility than others. If compression effiency is what you concern most, HEVC (H265) is your best video codec with virtually lossless quality and 65.36% file size off. The only downside is that HEVC is currently high demanding on your hardware configurations for HEVC playback. So make decision after you read the side-by-side comparison between H265 and H264 if you have no idea which to choose.
If the video converter software you're using doesn't support H264 or HEVC video codecs, take the all-in-one MacX Video Converter Pro into consideration. This is an all-round video processing tool capable of helping you convert any video to H264, HEVC, VP8, VP9, MPEG-4, MPEG-2, MP4, MOV, MKV, FLV, AVI, etc. 180+ video and 14+ audio formats thanks to 370+ video codecs supports. What's plus, you can also shrink and reduce 4K MP4, MKV, AVCHD, etc. video file size via codec conversion, video editing (trim/crop) and parameter adjustment (lower 4K to 1080p, tweak frame rate/bit rate...) at 10% - 80% compression ratio. Output video quality can be maximumly reserved to 98% - 100% (High Quality Engine) if you only choose editing or two of three compression methods.
How to Convert Video to Visually Lossless Video Codec
Step 1: Free download and run this video codec converter. If your computer supports AMD APP or Nvidia (NVENC/CUDA), the "Hardware Encoder" option will be automatically ticked at the lower right side of the main interface. 
Step 2: Tap "Video" button to import videos. Drag-and-drop is also supported.
Step 3: Choose the output video format with best virtually lossless video codecs H264 or HEVC based on your specific needs.
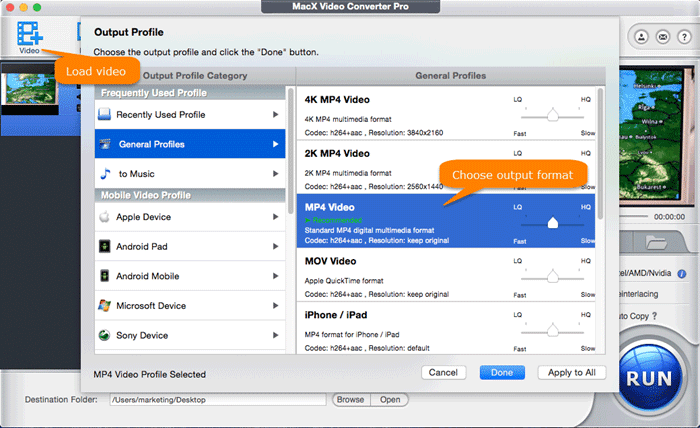
Step 4: Tap "RUN" button to begin transcoding video to best lossless video codec at GPU hardware accelerated speed. You can see the detailed conversion average frame rate shown on the conversion window.
Part 3. FAQs about Lossless Video Codec Formats
What is the best lossless video codec?
HEVC (H.265) is properly the latest and the better compression codec than others. HEVC is the best lossless video codec in terms of efficiency, performance, and compatibility. Most modern software and hardware have support for HEVC lossless video codec. The latest codec AV1 is a viable option.
Is MP4 lossy or lossless?
MP4 is a lossy video container format. When you store the same audio or video file to MP4 container, you lose a little bit of data and quality. However, you can not tell the difference after re-encoding an MP4 video file.
Which video codec is best for quality?
For a given compression ratio, H.265(HEVC) is the best codec for quality and is widely used for 4K UHD content. H.265 is the best video codec when it comes to the best trade-off between compression and quality. VP9 is more commonly used for YouTube, Android, Google Chrome, and web browsers. In fact, there's no the best answer because it depends on the source material, the bitrate, and you demands.
Is H.264 lossy or lossless?
H.264 is commonly used for lossy compression. It also offers lossless compression. FFmpeg has a "lossless" mode for x264. If you use libx264rgb ffmpeg encoder with format of pixel rgb24, you won't lose video quality.








